
Weight gain during pregnancy varies from one woman to the next and what is right for you will be based on whether you began your pregnancy as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Your doctor can advise you on the healthiest path for you. Weight gain during pregnancy can influence the weight of your baby at birth; remember that an extra-large baby is not healthier than a baby born of average weight.
What does a healthy weight gain in pregnancy look like?
Every pregnancy is different, but an average weight gain during pregnancy generally ranges between 11.5-16kg. This pregnancy weight gain is made up of baby weight and fat reserves to feed your baby in your uterus and for breastfeeding. If you are overweight or underweight, your doctor may adjust this, it’s just important that you stick within the recommended range.
Try for a slow and steady pregnancy weight gain but remember that all women gain weight at different rates. It’s important to follow your doctor’s recommendation because either too little or too much pregnancy weight gain may lead to difficulties. It’s also important to remember that it’s the quality of the foods you eat as well as the quantity that matters.
Weight gain guidelines during pregnancy
The recommended weight gain during pregnancy depends on mum’s pre-pregnancy weight in relation to body height (body mass index, BMI). The table below outlines the recommended weight gain during pregnancy depending on your pre-pregnancy BMI:
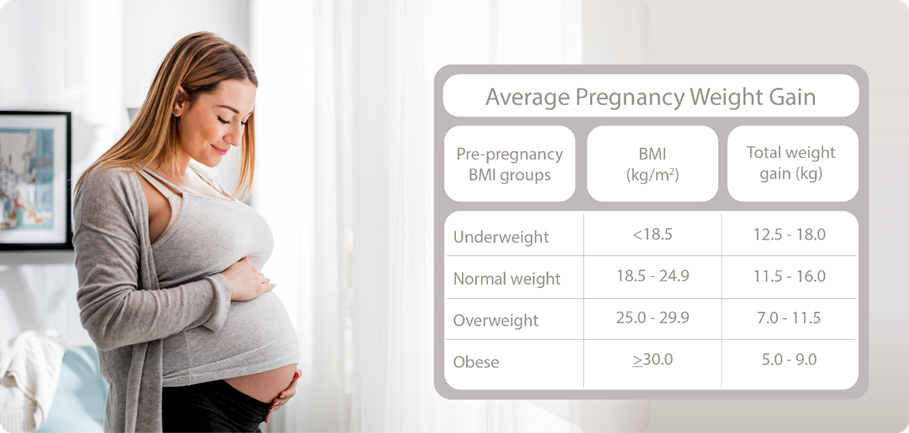
These recommended ranges represent an average weight gain during pregnancy and while it applies to all women, variations in women’s height, as well as different racial or ethnic backgrounds should be considered. Calculations will also differ for multiple pregnancies and it’s best to talk to your healthcare professional for guidance on individualised weight gain.
Weight gain in first trimester
In the first few months, early pregnancy weight gain will be minimal for most women, maybe 1-2 kilograms. Some mums-to-be may even lose a little weight because of vomiting and nausea that comes from morning sickness. Don’t worry – your baby’s nutrient needs will still be met by your body even if you have trouble keeping food down. If you have concerns about your weight during the period of morning sickness always discuss this with your doctor as there may be solutions, you had not thought of.
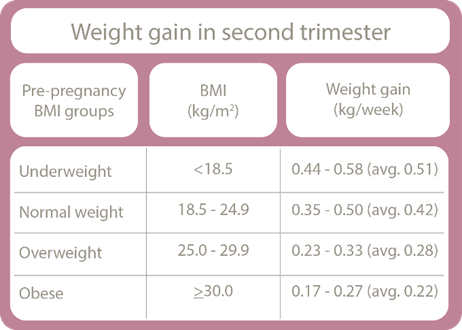
Weight gain in second trimester
If you’re starting from a healthy weight pre-pregnancy, the average weight gain in the second trimester is about 6.3kg. It is important for expectant mothers to focus on a balanced diet rich in nutrients and to consult with healthcare providers to ensure that weight gain is within healthy guidelines, as individual needs may vary.
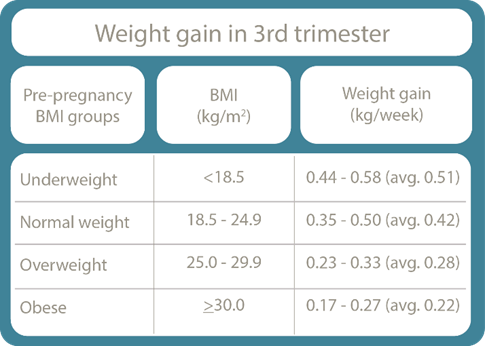
Weight gain in last trimester
During the third trimester of pregnancy, weight gain continues at around the same rate as experienced in the second trimester. On average, women may gain about 0.35 to 0.5 kilogram (0.8 to 1.1 pounds) per week during this period, contributing to the overall recommended weight gain of 11 to 16 kilograms (25 to 35 pounds) for women with a normal pre-pregnancy weight. This weight gain supports the growth and development of the foetus, as well as the formation of essential reserves for breastfeeding. As each pregnancy is unique, use this as a guide only and talk to your healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Healthy pregnancy weight gain: Striking a balance
- Just right. When you gain weight appropriately, it is one less thing that could cause complications. Your healthcare professional will estimate the right amount of weight for you to gain based on your health and pre-pregnancy weight.
- Too little. Your growing baby needs nourishment, and you must eat enough for both of you. If you don’t gain enough weight, you may deprive your baby of nutrients needed for growth. So be sure to follow your doctor’s weight gain guidelines.
- Too much. Some women have been known to use pregnancy weight gain as an excuse to break all their healthy eating rules. That’s not a good idea as it puts extra stress on your heart and joints, increases your risk of backache and other health problems. Excess weight can make your recovery longer and affect your energy levels which you need when you have a newborn. Obesity is not only a health hazard for you. Your little one, who is yet to be born, may also feel the negative effects of it too, including growth, development and general health challenges.
Tips for healthy weight gain during pregnancy
- Before you get pregnant, check your weight. Being a healthy weight before you conceive is best for you and your future baby.
- Dieting while pregnant is not advisable: you run the risk of drastically cutting down on you and your baby’s essential nutrients and could affect your baby’s development. Consult a dietitian if you want guidance on your diet during pregnancy.
- Maintain a healthy balanced diet, rich in protein. Proteins are the building blocks of our bodies so when you’re making a whole other little body inside you, it becomes quite an important nutrient in your diet.
- Make sure your diet is rich in foods containing folic acid, iron and calcium. Folic acid plays an important role in neural tube development, while iron and calcium are important for blood cells and bone development for you and your baby. Supplements are often recommended prior to getting pregnant.
- If you want to change your diet or workout routine, consult your doctor first. A moderate exercise routine spread out across the week may be very beneficial to help maintain strength and stamina throughout your pregnancy and childbirth.
- Take pride in your pregnancy weight increase because it means a healthy growing baby, if you have any concern you are gaining too much or too little weight talk to your doctor or a dietitian.
How to achieve a healthy weight gain in pregnancy
While it does take energy to develop a healthy baby, that energy can come from the food you eat, or from your existing weight stores. A mum-to-be does not need to eat twice as much. During your pregnancy, your energy demands will increase over time.
- First trimester - There is no need to change your energy intake during the first trimester;
- Second trimester - You will need an extra 1400 kilojoules per day on top of your pre-pregnancy dietary intake;
- Third trimester – You will need an extra 1900 kilojoules per day in your last trimester.
However, this can be different depending on your starting weight, so it’s always good to ask your healthcare professional what is right for you. To put this into perspective, the average adult should be consuming around 8700 kilojoules per day. So these additional kilojoule requirements in the 2nd and 3rd trimester means you don’t need to double your diet – it’s just eating a little more.
Having twins? Learn about eating for three
Frequently asked questions about pregnancy weight gain
How much weight do you gain in pregnancy
During pregnancy, most women that are a healthy weight before their pregnancy, gain between 11.5 to 16 kilograms (25 to 35 pounds). This pregnancy weight gain supports the developing baby, placenta, amniotic fluid, and maternal tissue. Individual needs will vary, so it’s essential to talk to your doctor or midwife for personalised guidance.
When do you start gaining weight in pregnancy
Every pregnancy is different but weight gain typically begins for most mums-to-be in the second trimester. Although some women may notice earlier changes, especially if this is not your first pregnancy. Early pregnancy weight gain can be attributed to increased blood volume, hormonal changes, and the development of the placenta. Regular check-ups can help monitor weight changes throughout pregnancy.
How to maintain weight while pregnant
Maintaining a healthy weight gain in pregnancy involves balanced nutrition and regular physical activity. Focus on consuming nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Additionally, regular moderate exercise, like walking or swimming, can help manage weight while ensuring the health of both mum and baby.
How much weight is normal to gain in pregnancy
The normal weight gain during pregnancy varies based on pre-pregnancy starting weight. An average weight gain during pregnancy for women starting from a healthy weight, is 11.5 to 16 kilograms (25 to 35 pounds). Women who are underweight may need to gain more, while women who are overweight should aim for less. A doctor or dietitian can help give personalised recommendations that meet specific pregnancy needs.
How much weight should you gain in first trimester
For most women, there is not much weight gained in the first trimester. Any early pregnancy weight gain is often due to increased blood volume and hormonal changes rather than significant foetal growth. Each woman's experience is unique, so discussing weight gain with your doctor will help you get your weight gain goal correct.
How much weight should you gain in second trimester
Weight gain in the second trimester typically occurs at about 1.4-2.0 kg per month (3.3 - 4.5 pounds). This period supports the rapid growth of the baby and placenta. Regular monitoring and healthy eating habits are crucial to ensure appropriate pregnancy weight gain during this stage.
How much weight should you gain in third trimester
Weight gain in the last trimester is at a similar rate to weight gain in the second trimester. Women can experience a typical weight gain of about 1.4-2.0 kg per month (3.3 - 4.5 pounds). This pregnancy weight gain is primarily due to the growing baby, increased amniotic fluid, and maternal fat stores. It's important to maintain a balanced diet and stay active, while also monitoring weight closely with a healthcare professional.
Sources
- NHMRC NRV Website. Accessed at https://www.nrv.gov.au/dietary-energy.
- Australian Dietary Guidelines Website. Accessed at Healthy eating when you’re pregnant or breastfeeding | Eat For Health
- Pregnancy, Birth & Baby Website. Accessed at Weight gain in pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby






